Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is shaping the future of secure connectivity by enforcing strict identity verification and least-privilege access. As digital landscapes evolve, ZTNA adapts to dynamic environments, protecting users and resources from sophisticated threats. Its integration with AI, automation, and cloud-native solutions ensures scalability, making ZTNA essential for navigating the complexities of modern cybersecurity in a connected world.
Introduction
In today’s world, cyber threats evolve rapidly, necessitating a flexible and resilient cybersecurity approach. Traditional security models—which once relied on a robust perimeter to defend against external threats—are losing efficacy. Modern threats can infiltrate outside and inside the organization, highlighting an urgent need for innovation. Enter zero trust network access (ZTNA), a cutting-edge framework that revolutionizes data protection by assuming every attempt to access the network might be a potential threat. This paradigm shift is becoming essential for enterprises aiming to safeguard sensitive information effectively in an ever-changing digital landscape.
Global trends like remote work have increased security challenges for IT departments. ZTNA offers a solution by ensuring that only authenticated users access critical resources, enhancing security, and supporting dynamic work environments. This is crucial as the digital frontier expands.
Understanding Zero Trust Network Access
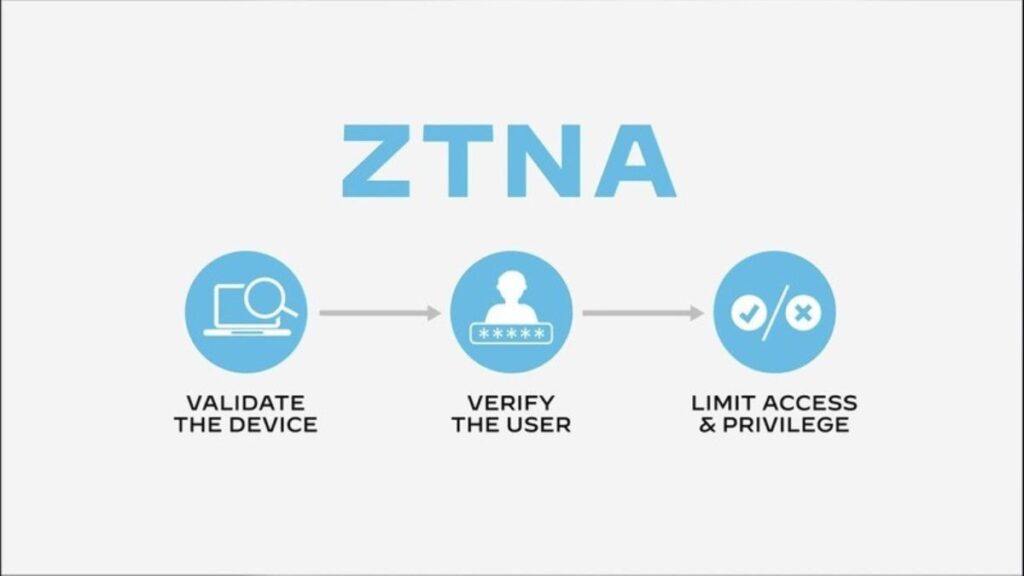
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) is not merely a set of technologies but a holistic security philosophy centered around the premise that trust is never inherent; it must be continually earned and verified. Unlike traditional security models that grant access once a user is inside the network, ZTNA assumes the network is always vulnerable to threats. It requires every user—inside or outside the organization’s boundaries—to be authenticated and authorized whenever they attempt to access data or applications. This approach substantially minimizes the risk of unauthorized access, ensuring a more robust defense strategy in today’s complex computing environments.
Why ZTNA is Gaining Traction
There are several reasons why ZTNA is becoming more and more popular. Chief among them is the alarming rise in cybersecurity attacks, which continue to escalate in frequency and complexity. According to Cybersecurity Trends, these threats quickly evolve, necessitating a more dynamic, adaptable approach to network security. Simultaneously, the global shift towards remote work—accelerated by the pandemic—has underscored the need for secure remote access solutions. ZTNA’s robust security framework addresses these challenges head-on, offering a more secure alternative to traditional VPNs by ensuring rigorous identity verification and access control. Consequently, many organizations are adopting ZTNA to bolster their cybersecurity defenses and support a shifting workplace dynamic.
Key Components of ZTNA
The architecture of ZTNA is built upon several foundational components. Firstly, identity verification is crucial; only permitted users can access specific data sets and applications. Each user’s identity is meticulously authenticated using multiple factors, thus preventing unauthorized or harmful access. Access management forms the next layer, implementing strict policy enforcement to regulate and control user privileges. Furthermore, ZTNA necessitates continuous monitoring, maintaining a vigilant watch over user behavior throughout each session. This component is essential for quickly identifying unusual activity and potential threats, allowing for swift intervention and damage mitigation.
Benefits of Implementing ZTNA
By adopting ZTNA, organizations unlock a wealth of benefits. An improved security posture, which lowers the chance of breaches and data leaks, is a significant benefit. ZTNA’s adaptable framework is highly flexible, integrating well with hybrid and cloud-based infrastructures to offer scalable security that grows alongside the organization. According to Technological Advances in Security, these enhancements in security technologies bolster ZTNA’s efficacy, reinforcing its appeal. As threats continue to evolve, ZTNA empowers businesses to remain agile and responsive, safeguarding against unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of their digital assets.
Challenges Faced by Organizations
Despite its many advantages, ZTNA implementation presents particular challenges. The initial investment can be substantial, demanding technological resources and skilled personnel to execute the deployment effectively. Integration issues may arise as companies attempt to retrofit ZTNA onto existing systems, especially if those systems need to be updated or compatible with newer technologies. Additionally, seamless transition requires detailed planning and change management to address potential disruptions. However, businesses that thoroughly prepare and consult with cybersecurity experts can navigate these challenges, benefiting from a robust, future-proof security model.
Real-World Applications of ZTNA
ZTNA’s applicability is diverse, spanning numerous industries where security is paramount. In healthcare, safeguarding patient data against breaches is critical; ZTNA protects by ensuring only authorized medical staff access sensitive information. Financial institutions managing vast amounts of confidential data leverage ZTNA to safeguard transactions and customer records from breaches and fraud. Each successful case study highlights the framework’s flexibility and effectiveness, illustrating its role as a cornerstone in modern cybersecurity strategies across varied sectors.
The Basics of Machine Learning and AI
The growing integration of AI and ML technologies greatly expands ZTNA’s potential. These technologies facilitate real-time data analysis, quickly detecting suspicious activities and abnormal behavior patterns that could signal security threats. By automating response mechanisms, AI and ML enhance security frameworks’ reactive and proactive capabilities, ensuring a more efficient defense against cyber-attacks. As these technologies progress, their continued integration with ZTNA promises even more significant advancements in security, paving the way for more sophisticated threat detection and response models.
Best Practices for Adopting ZTNA Strategies
To successfully implement ZTNA, organizations should begin with a comprehensive security risk assessment, identifying vulnerabilities and potential attack entry points. It’s vital to establish clear, robust policies for access management, aligning them with the organization’s specific security requirements and business goals. Continuous security monitoring and regular protocol evaluation are crucial in adapting to emergent threats. By tailoring ZTNA strategies to the unique needs of their businesses, companies can ensure resilience and longevity in their cybersecurity measures, ultimately fostering a safer, more secure environment.